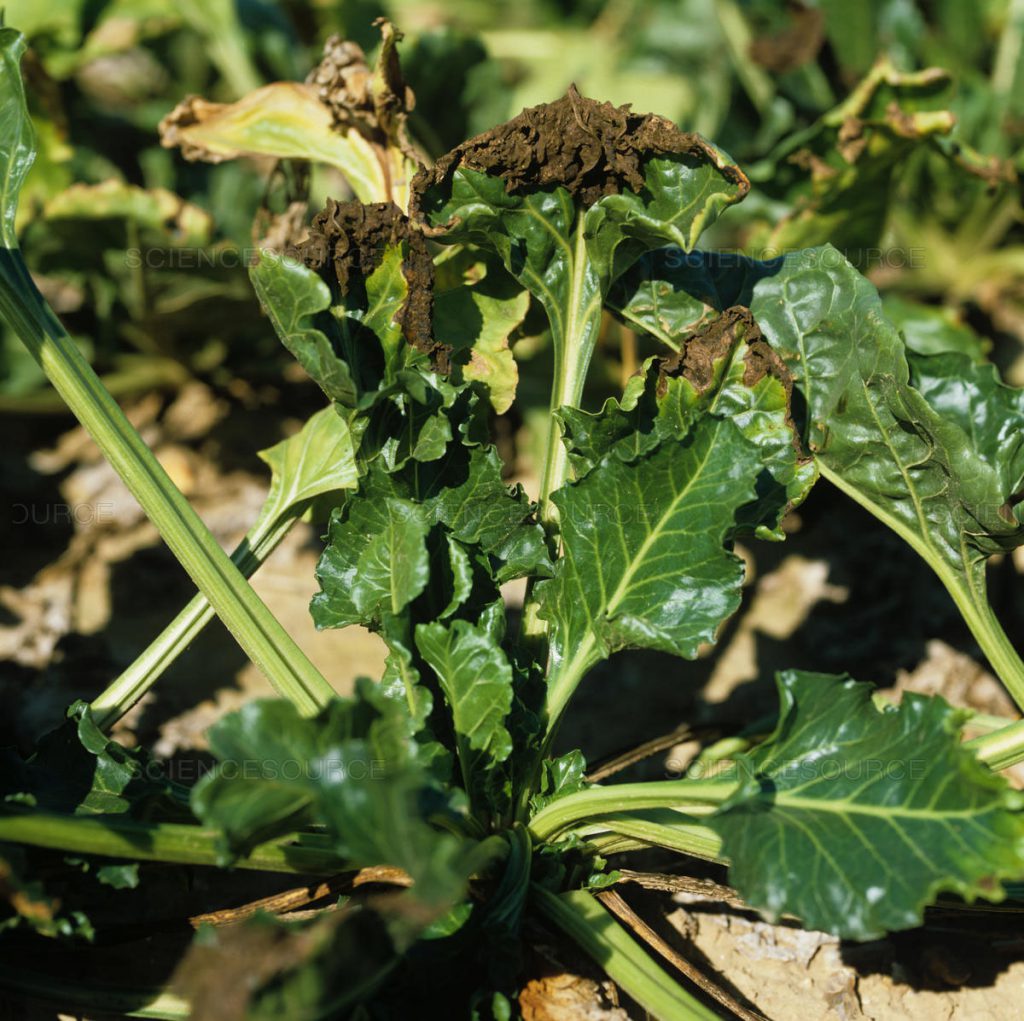
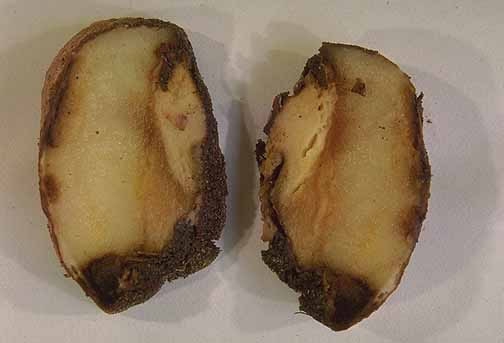
In Greece, bacterial soft rot can cause significant damage due to the favorable conditions (high temperature, heavy irrigation).
Scientific name: Erwinia carotovora
Other name: Soft rot, stem rot, bacterial stem rot
Greek name: Μαλακή Σήψη Τεύτλων
Symptoms
Bacterial soft rot affects the roots and stems. A pinkish-brown rot develops on the affected roots, which then takes over the entire root. Brownish lesions may also appear on the stems.
As it is difficult to identify affected plants before the rot is too advanced, the infestation may be revealed at harvest, leading to problems during beet preservation and extraction.
Pathogen – Growth conditions
Bacterial soft rots are caused by strains of the bacterium Erwinia carotovora. The bacteria are spread by insects, tools, rain, irrigation water, clothing and contaminated plant tissue. They enter the plant from a wound and occupy the vascular bundles of the root and stems. The disease is more pronounced and more frequent in soils with poor drainage and overwatering. After harvest, any wound can cause bacterial rot during storage. High temperatures (25-30 degrees Celsius) favor the development of such bacterial infections.
Treatment
Wounds should be avoided as far as possible during cultivation, harvest and afterwards. Severely affected plants should also be removed and destroyed. The residues of the previous crop should also be destroyed and measures should be taken to reduce moisture.
Source
www.bayercropscience.gr
Bacterial soft rot, bacterial stem rot
Wikipedia – Erwinia
Microbe Wiki – Erwinia carotovora
Tags: PLANT DISEASE