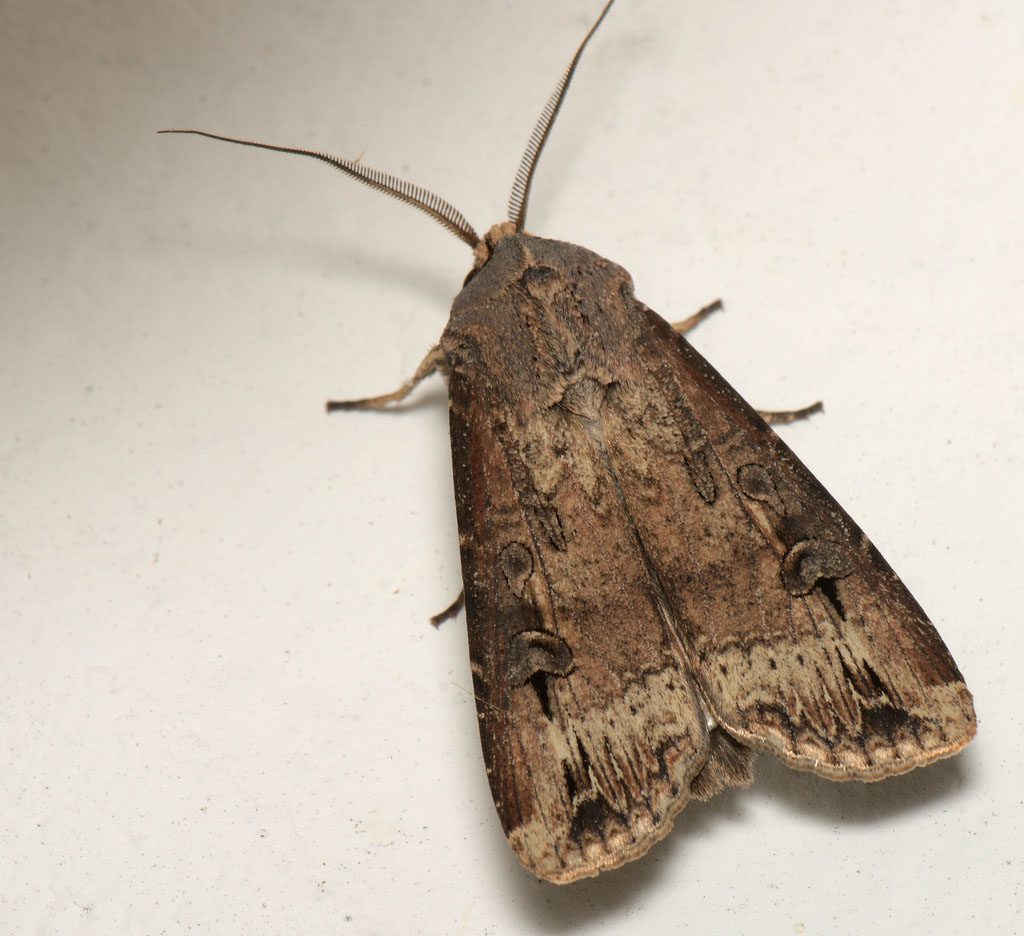
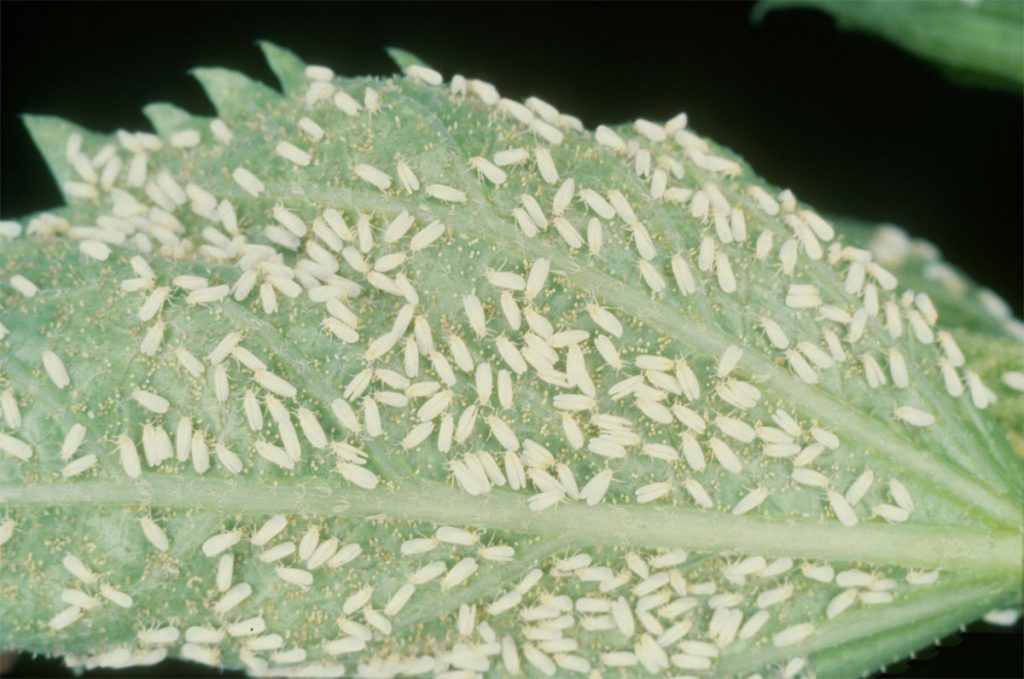
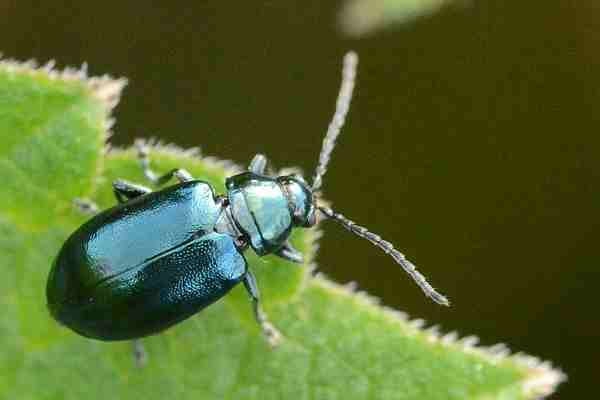
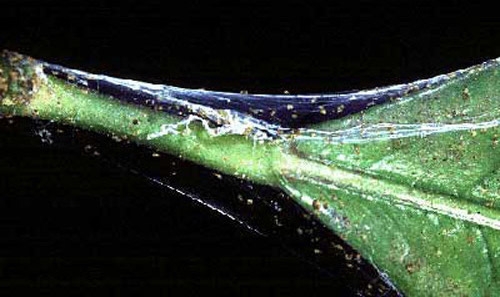
The hornbeam mite is widespread mainly in the area of Corinth, Greece. It directly damages buds, causing necrosis, leaves, stems and shoots by forming necrotic spots.
Scientific name: Eutetranychus carpini, Tetranychus urticae
Greek name: Κίτρινος τετάνυχος
Damage
Hornbeam mite directly damages buds, causing necrosis, leaves, stems and shoots by forming necrotic spots. It can also cause shortening, deformation and tearing of leaves, regional necrosis of the lamina, which slowly takes over the entire leaf surface. This leads to a reduction in the quantity and quality of production, unevenness and delays in the ripening of the grapes and the wood of the vines. When they grow in large populations, the infestation can be particularly severe and the stalk takes on a wilting appearance.
Enemy
Unlike the common spider mite, the hornbeam mite attacks the vine as early as spring to autumn, completing 6-8 generations. It spreads as a fertilized female in colonies under the dry bark of stumps or in natural shelters. In spring they become active and multiply. It lay eggs on the undersurface of leaves, along the main ribs.
It is sensitive to high temperatures and continuous heavy rains.
Treatment
Winter spraying with suitable insecticides against the overwintering forms is recommended as a basic treatment. During the growing season, treatments in the vineyard with acaricides help to prevent the development of spider mite populations.
Source
www.bayercropscience.gr
Eotetranychus carpini – Hornbeam mite – (Oudemans, 1905)
Tags: PLANTS ENEMY