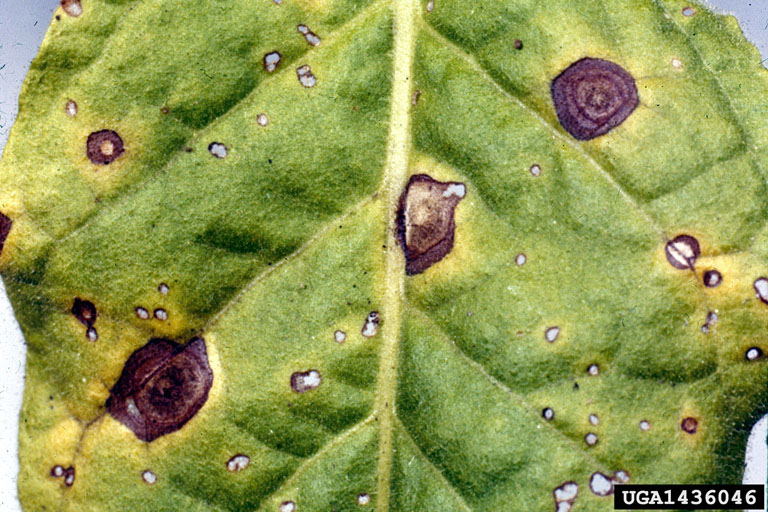
Potato late blight attacks the green parts and tubers of potatoes.
Scientific name: Phytophthora infestans
Other name: late blight, potato blight
Greek name: Περονόσπορος της Πατάτας
Potato late blight symptoms
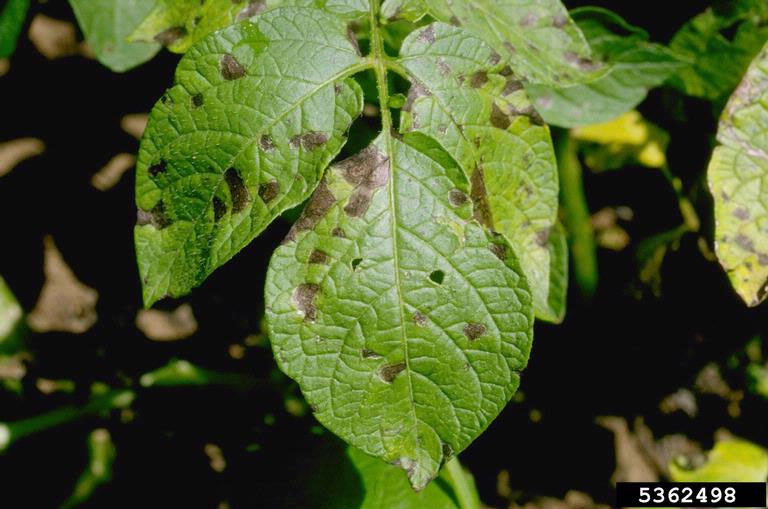
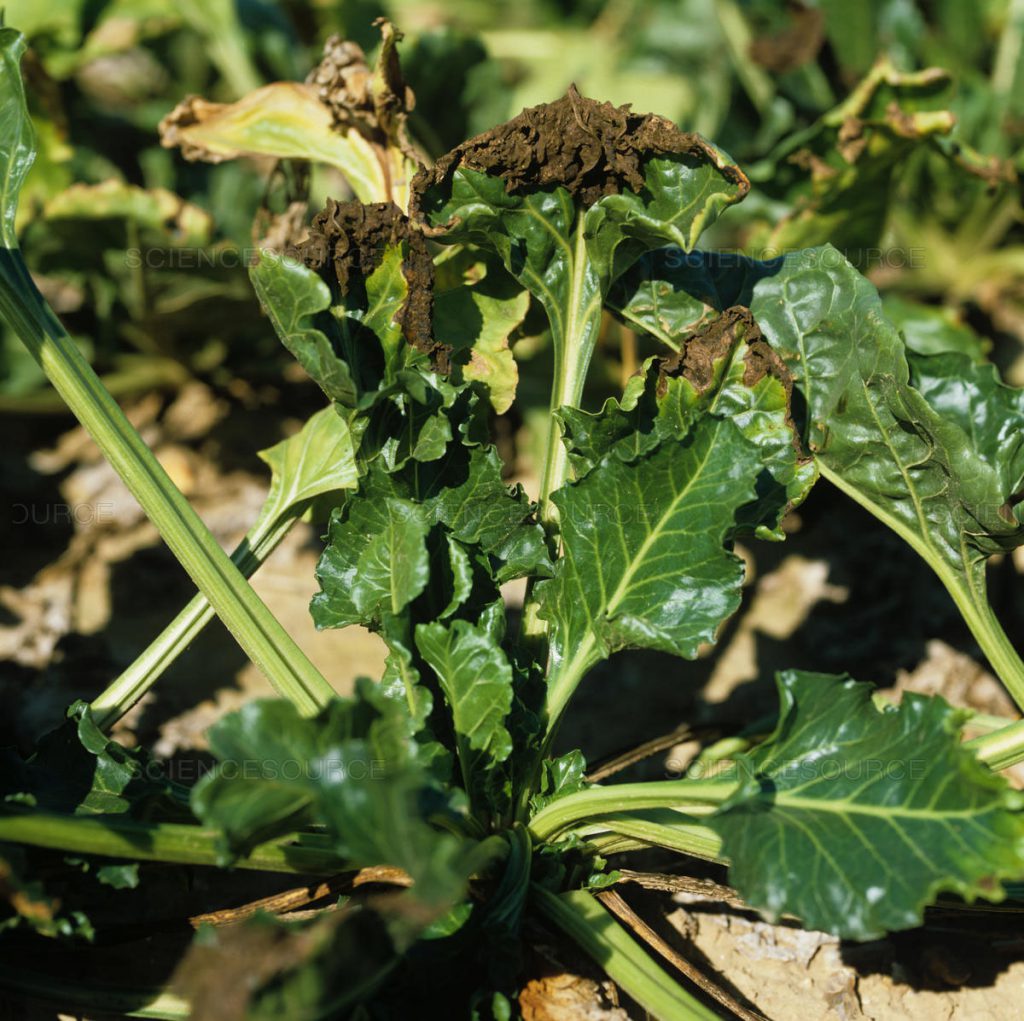
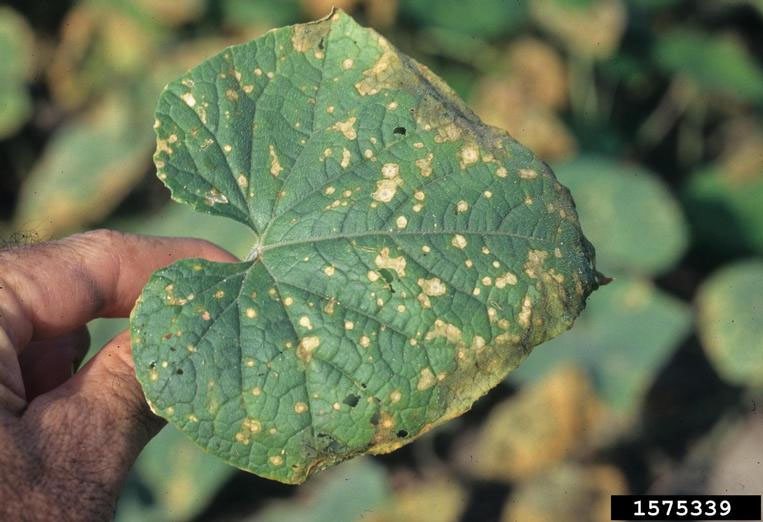
Potato late blight attacks the green parts and tubers of the potato. The infestation starts on the lower leaves, where yellowish, irregularly shaped spots appear. These areas then turn brown and dry out. Under moist conditions, the white flesh (dehiscence) of the fungus can be seen on the back surface of the leaves.
Potato tubers are also affected and show extensive, irregular, dark spots on the outside. Internally, the tissues under the affected areas turn the color of rust and rot (dry and wet rot).
Pathogen – Growth conditions
Potato late blight is caused by the fungus Phytophthora infestans. It requires moist and cool weather (17-20 °C) for its growth. Under such favorable conditions the disease can spread very quickly, destroying the plants.
Treatment
A program of preventive measures is required to control potato late blight especially in areas with favorable conditions for its development (e.g. western Greece).
Protection of young vegetation is important to prevent the disease from establishing in the field. Good spraying and protection of young growing vegetation is also of particular importance, especially when contact sprays are used.
It is recommended to follow the instructions in the Agricultural Warnings as to expected infestation, weather conditions and timing of intervention. In critical periods for the spread of the disease (e.g. in rainy weather conditions with temperatures of 20-25 °C) it is recommended to give preference to mixtures with inter-systemic products.
Source
www.bayercropscience.gr
Phytophthora infestans
Tags: PLANT DISEASE • POTATO • POTATOES