Rhizoctonia root rot is a disease that occurs to a small extent throughout Europe. Beet destruction can be total when infection occurs early.
Scientific name: Corticium solani, Rhizoctonia solani var. betae
Other name: Crown rot
Greek name: Καστανή σήψη τεύτλων
Symptoms
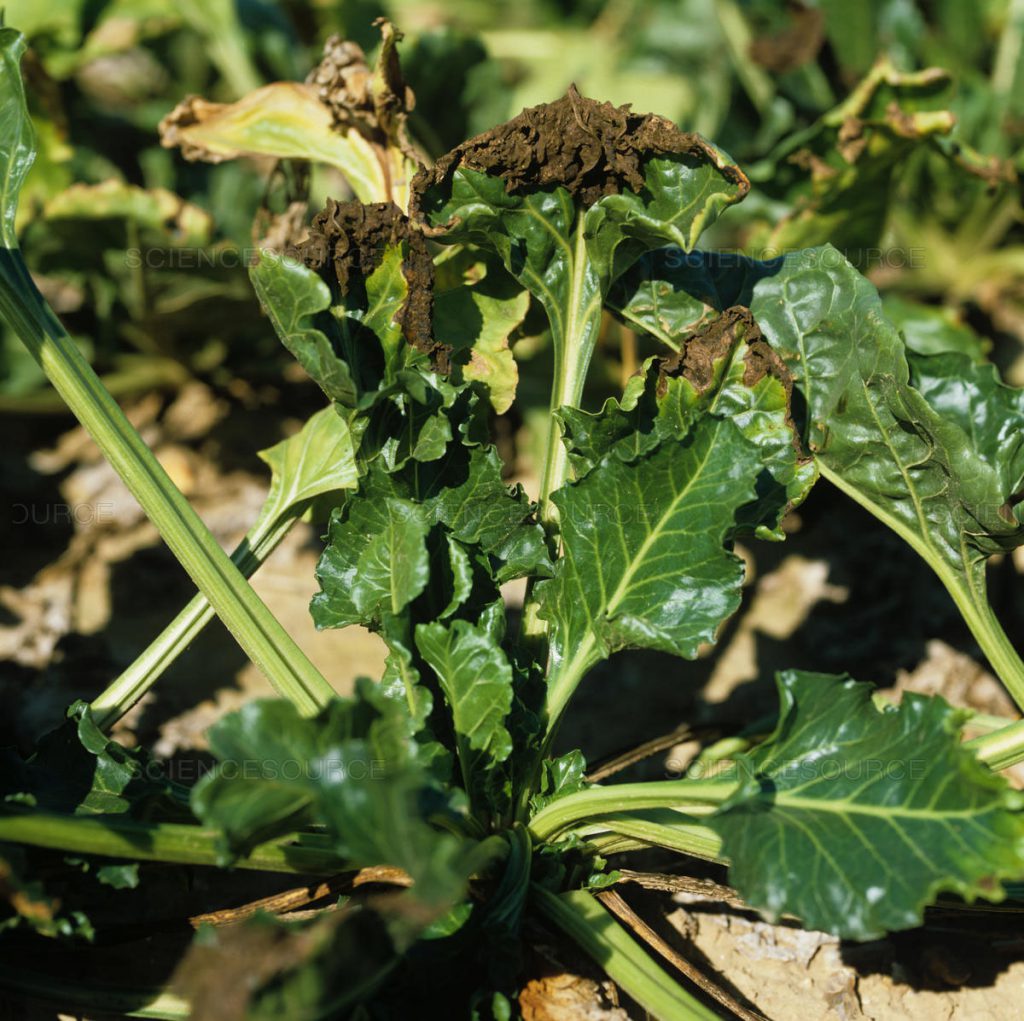
Rhizoctonia root rot disease, caused by a soil fungus, occurs in circular patches within sugar beet fields. At first it is manifested by wilting of the plants which progressively leads to complete necrosis of the foliage.
A more or less deep brownish rot is observed on the root, depending on the degree of disease progression.
Pathogen – Conditions of growth
The fungus persists in the soil in the form of sclerotia. From these, the mycelium germinates and attacks the surface of the root and then progressively penetrates it, causing it to rot, sometimes to the point of total destruction of the plant. The disease manifests itself quite early and its spread is favored by poor soil structure and excessive moisture and by high temperatures.
Treatment
Cultivation measures are recommended, such as improving the soil structure, extending the rotation period and using resistant varieties.
Source
www.bayercropscience.gr
Rhizoctonia solani
Control of Rhizoctonia solani in Sugar Beet and Effect of Fungicide Application and Plant Cultivar on Inoculum Potential in the Soil
Rhizoctonia Root Rot
Rhizoctonia Crown and Root Rot of Table beet
Management of Rhizoctonia Root and Crown Rot of Sugar Beet
Tags: BEETROOT • BEETROOTS • PLANT DISEASE